Table of Contents
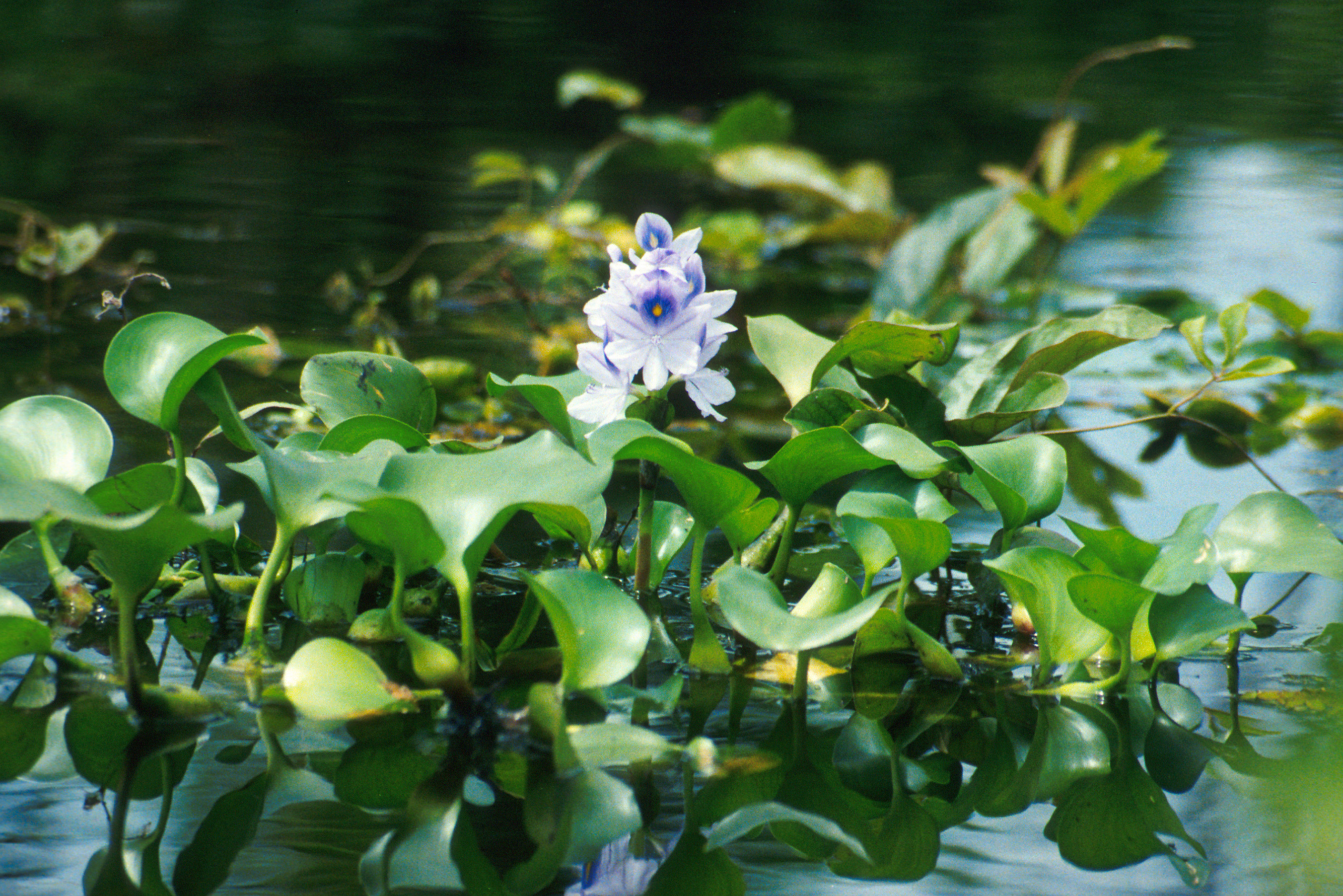 |
| Water hyacinth. Photo by Ted Center. Image from WikiMedia Commons and is part of the public domain. |
Description
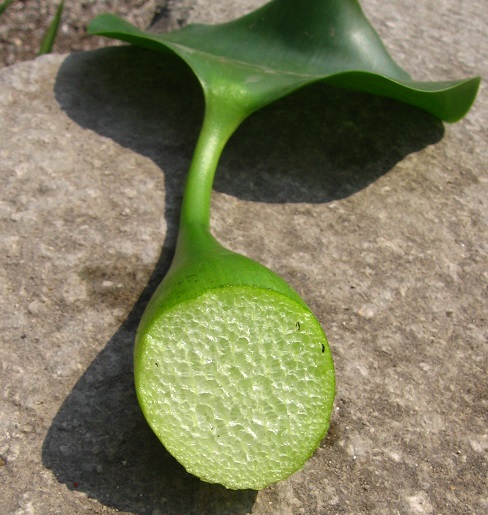 |
| Spongy petioles. Photo by Jacopo Prisco. Image from WikiMedia Commons. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |
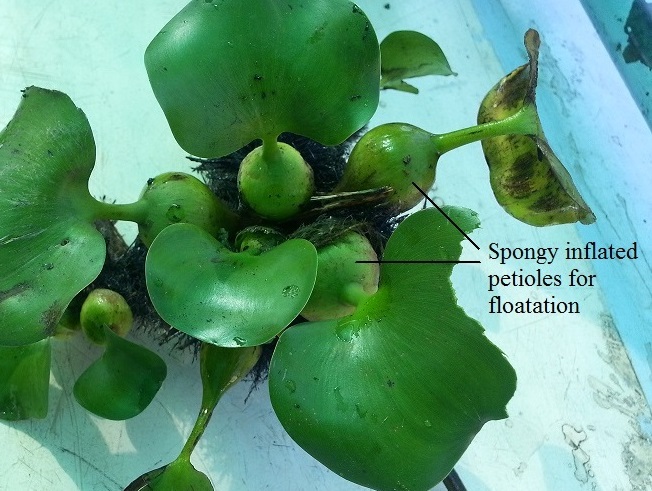 |
| Spongy stalks of water hyacinth. Photo by Arunravi.signs. Image from WikiMedia Commons. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |
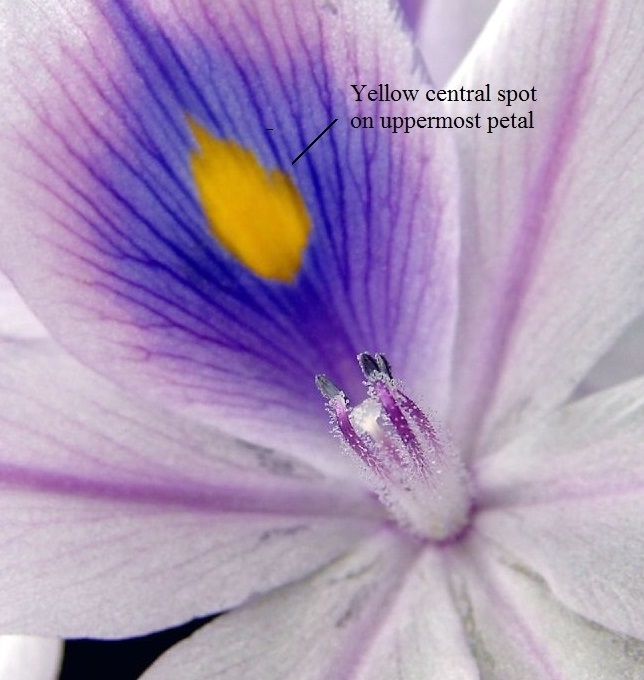 |
| Water hyacinth flower. Photo by aussiegall. Image from WikiMedia Commons. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license. |
The species name crassipes is derived from latin, meaning thick-footed of thick-stalked. 1 Eichhornia crassipes is more commonly known as the (common) water hyacinth, is a free floating aquatic plant that generally grows to a height of 0.5m. 2, 3 It can also occasionally be found rooted in soil on banks of water bodies. It has rounded, thick and glossy dark green leaves that are attached to spongy, inflated petioles. 2, 3 The root system lies beneath the water, and is feathery and heavily branched. Its attractive flowers have 6 purplish blue or lavender to pinkish petals, and the uppermost petal has a yellow, blue-bordered splotch in the centre. 2, 3 The flowers grow on a terminal spike in clusters of 8-15. 2, 3
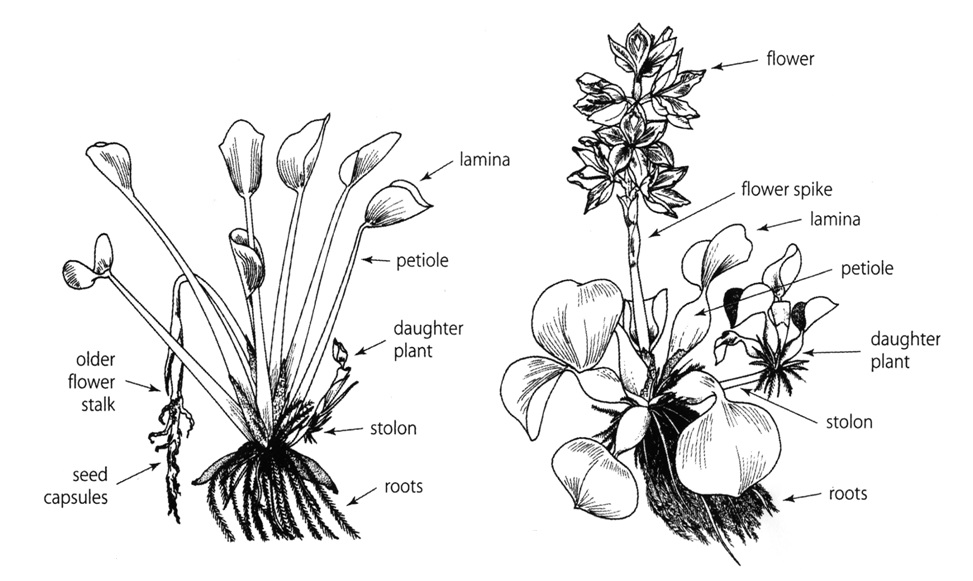 |
| Diagram of water hyacinth anatomy. Image adapted from Julien, M.H., Griffiths, M.W. & Wright, A.D., 1999. Biological control of water hyacinth: The weevils Neochetina bruchi and N. eichhorniae: biologies, host ranges, and rearing, releasing and monitoring techniques for biological control of Eichhornia crassipes, Canberra: The Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research. |
Distribution
The water hyacinth is native to the Amazon basin, but can now be found in more than 50 countries across the tropics and subtropics between 39°N and 39°S. 4, 5 It was introduced outside its native range as an ornamental plant due its beautiful flowers. 4, 5 The water hyacinth is now considered a highly problematic invasive species outside of its native range, and is ranked as one of the top 100 invasive species in the Global Invasive Species Database. 2 Due to its invasive nature, the import of water hyacinth has been banned in many parts of the world, such as New Zealand, Australia and parts of the US. 6, 7 As temperatures climb due to global warming, the distribution of water hyacinth may even expand into higher latitudes where their growth was once inhibited by climatic factors. 4
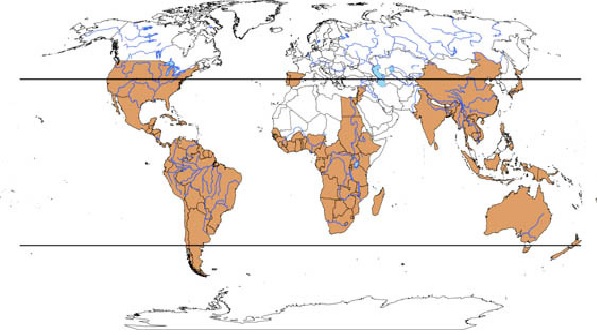 |
| Distribution of water hyacinth (orange indicates the presence of water hyacinth). Image adapted from Téllez, T., López, E., Granado, G., Pérez, E., López, R. & Guzmán, J., 2008. The water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes: an invasive plant in the Guadiana River Basin (Spain). Aquatic Invasions 3(1): 42-53. |
Habitat
Water hyacinth is a perennial aquatic herb that can grow in still or slow-flowing fresh water in tropical and subtropical climates, and even in temperate regions with milder winters. 8, 9 Its optimum growth occurs between 28°C and 30°C, and requires abundant nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium; however, it can tolerate a wide range of growth conditions. 8 It is widely prevalent in tropical and subtropical waters enriched by agricultural runoff, untreated wastes and deforestation. 10 It is especially pervasive in Southeast Asia, the southeastern United States, central and western Africa and Central America due to suitable growing conditions and the lack of natural predators. 10
Reproduction
 |
| Clones connected by a stolon. Photo by Leslie J. Mehrhoff, University of Connecticut. Image from Bugwood.org. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. |
Water hyacinth is one of the world’s fastest growing plants. It can form dense mats that cover entire bodies of water. 2, 3, 6
It can can reproduce vegetatively or sexually. 11, 12 However, in many areas, sexual reproduction is rare or even non-existent although flowers and seedlings may still be produced. 11, 12 This has been attributed mainly to the absence of suitable ecological conditions for fertilisation or germination of seedlings. 11, 12 The seeds are denser than water, hence they sink to the bottom or get caught in the dense mat of plants. 12 The floating mat of water hyacinth plants blocks sunlight from reaching the seeds in such conditions, preventing germination of seeds. 12
Asexual reproduction of water hyacinth occurs through stolons which form daughter plants. 2, 3 The stolons of water hyacinth have several nodes, and each node can produce a new daughter plant which can in turn produce more stolons. 2, 3 In the Nile river system, an adult plant can produce an average of 43 new daughter plants in 50 days. 13
Impacts of Water Hyacinth Invasions
| Water hyacinth invasion at Roodeplat Dam in South Africa. Photo by Chronoplast. Image from WikiMedia Commons. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |
Water hyacinth is listed by law as a noxious weed in a number of countries. It is the most widespread and damaging aquatic plant species in Africa; it is estimated that the economic impacts of the weed in Africa alone may be as much as US$100 million annually. 4, 14 Outside of its native range in South America, the water hyacinth has few natural enemies and can proliferate extremely rapidly. 4 At the peak of the infestation of Lake Victoria, the second largest freshwater lake in the world, it was estimated that the water hyacinth mat was growing at 3 hectares (roughly 24 Olympic sized swimming pools) per day. 15 The water hyacinth is also prevalent in the Mekong delta in Vietnam, Cambodia, Lao PDR and Thailand.
16 In Thailand and Vietnam, biological control methods and various legislations have been put in place to control the spread of water hyacinth, but the weed remains a problem in the region. 16 The socioeconomic impacts of water hyacinth invasions depend on the severity of the invasion. 10
Biodiversity
Due to its rapid rate of growth and reproduction, this weed can out-compete other aquatic plants. 2, 3, 4, 10, 16 The large dense floating mats of water hyacinth block sunlight and monopolise nutrients, killing submerged aquatic plants. 4, 10 The mats not only block sunlight, preventing phytoplankton and submerged plants from photosynthesising, they also prevent oxygen from dissolving into the water, thus causing an overall drop in dissolved oxygen concentrations. 4, 10 Aquatic organisms sensitive to changes in dissolved oxygen levels will be negatively affected. 4, 10However, the complex root systems and leaves of water hyacinth mats may also provide refuge for aquatic organisms, especially epiphytic invertebrates like snails and aquatic insects. 10 Fish population compositions can also be affected. 10 In some areas, fish populations have even increased due to the water hyacinth. 10 The overall effect of water hyacinth invasions on biodiversity is dependent on many factors. 10 The diagram below shows interactions between water hyacinth and other components of a freshwater community. The introduction of water hyacinth has can affect a freshwater ecosystem through its interactions with all these parts of the ecosystem, which interact with each other as well, making it difficult to predict the exact ecological effects of an invasion.
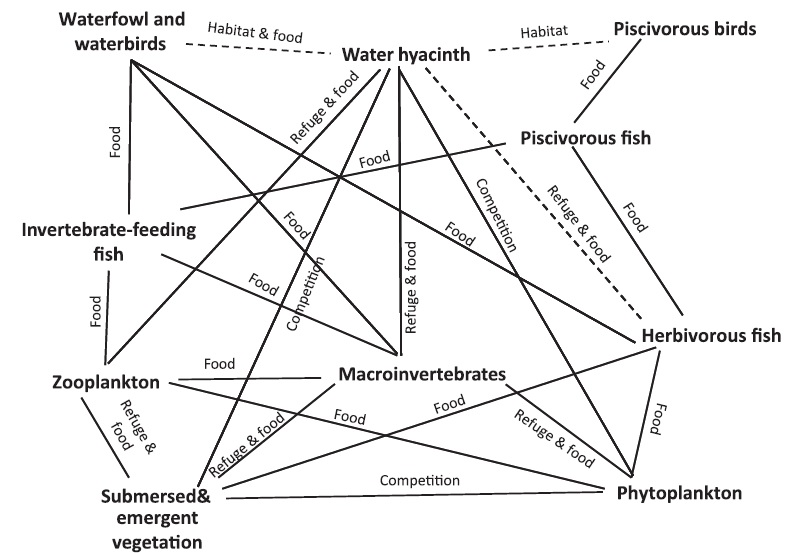 |
| Interactions between non-native water hyacinth and ecosystem. Image from Villamagna, A. M. & Murphy, B. R., 2010. Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A review. Freshwater Biology, 55(2): 282–298. |
Pests and Vectors
Water hyacinth mats have the effect of slowing water flow, creating suitable breeding grounds for mosquitoes that carry diseases such as malaria and human lymphatic filariasis, and snails which are vectors for schistosomiasis. 4 Incidence of cholera was also found to be positively correlated with water hyacinth cover in Nyanza Province in Kenya that borders Lake Victoria. 4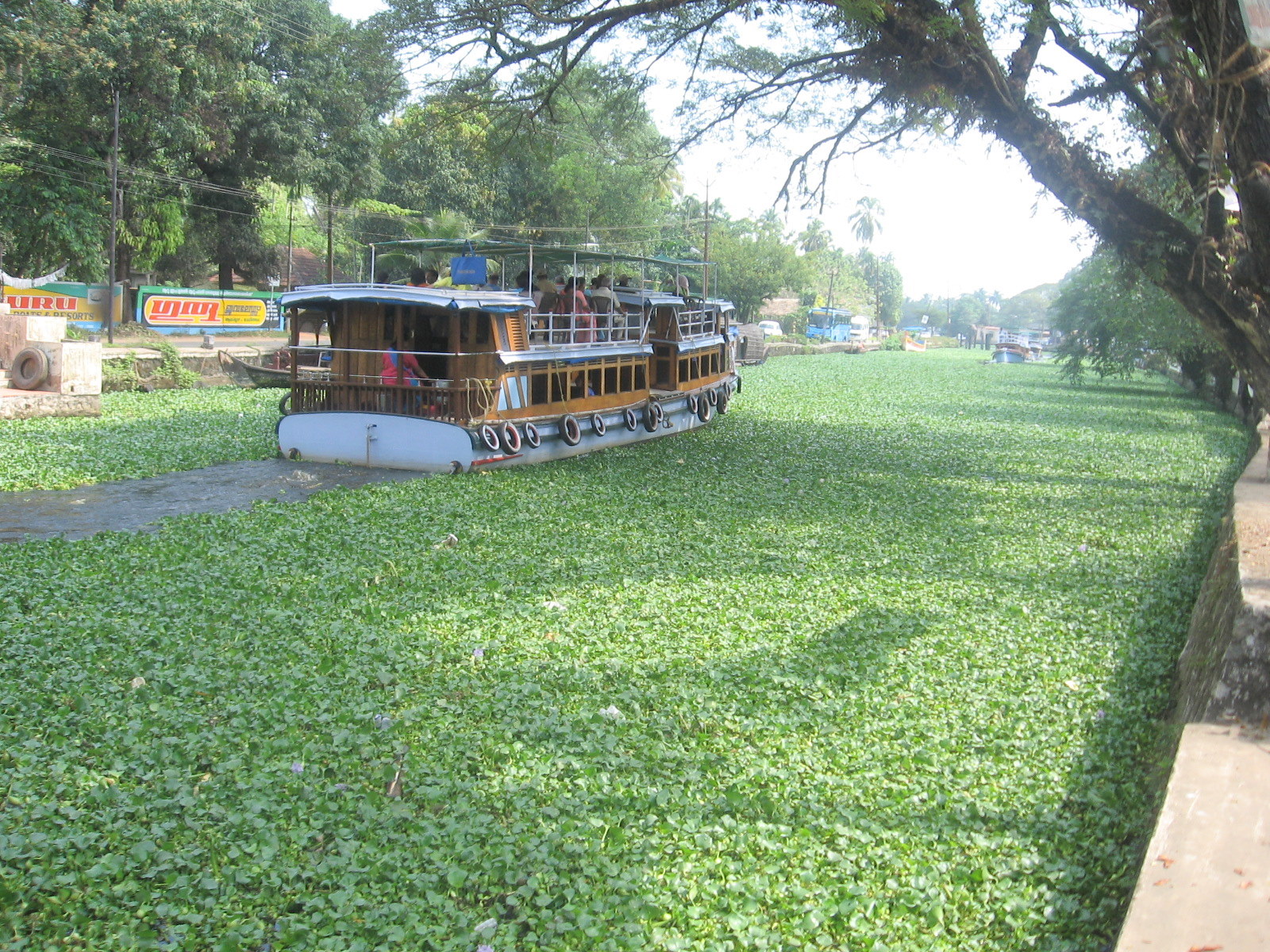 |
| A ferry wades through water hyacinth in an Alppuzha canal. Photo by P.K.Niyogi. Image from WikiMedia Commons, and is part of the public domain. |
Water hyacinth mainly impacts the economy by clogging waterways, disrupting ship and boat navigation and restricting access to water for recreation, fisheries, and tourism. 4, 10 In Kenya, water hyacinth mats rendered fishing grounds in Lake Victoria inaccessible, decreasing fish catch rates by 45%. 4 In parts of Nigeria and Cameroon, entire waterways have been rendered impassable due to this weed. 4, 10 In parts of India, water hyacinth blockages in irrigation channels reduce irrigation for crops and even cause flooding. 17 The plants can also get caught in hydropower dams: clearing water hyacinth from the hydroelectric dam at the Owen Falls in Uganda costs about US$1 million per year. 4, 18
Management of water hyacinth is also costly. 10 See control methods.
Water Quality
Water hyacinth invasions will cause a decrease in dissolved oxygen, but they are also able to absorb contaminants, heavy metals and excessive nutrients from the water column. 10 See phytoremediation.Water Hyacinth in Singapore
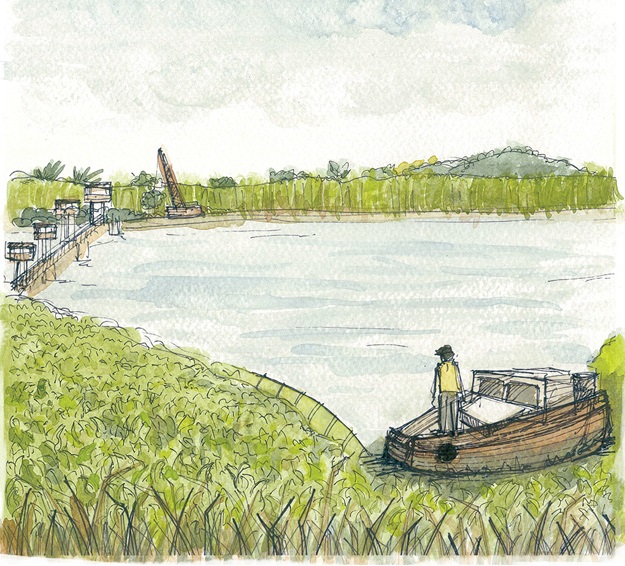 |
| Water hyacinths at the Kranji Reservoir in the 1970s. Image from Public Utilities Board [PUB], 2013. PUB annual report 2012/ 2013: Commemorating 50 years of water from the first drop. (Permission pending) |
Water hyacinth only became a problem in Singapore after the damming of the Kranji River to build the Kranji Reservoir. 19 The dam trapped wastes washed in from pig, poultry, vegetable and fish farms in the catchment area in the reservoir. 19 Water hyacinth thrived in the nutrient rich waters of the reservoir, prompting the Public Utilities Board (PUB) to take action. 19 Being a reservoir for drinking water, chemical management using herbicides was out of the question. Tug boats and machinery were employed to physically remove the plants. 19, 21 This proved only partially effective, because the removed plants were left on the banks of the reservoir, returning nutrients back into the water when the dead plants rotted. 19
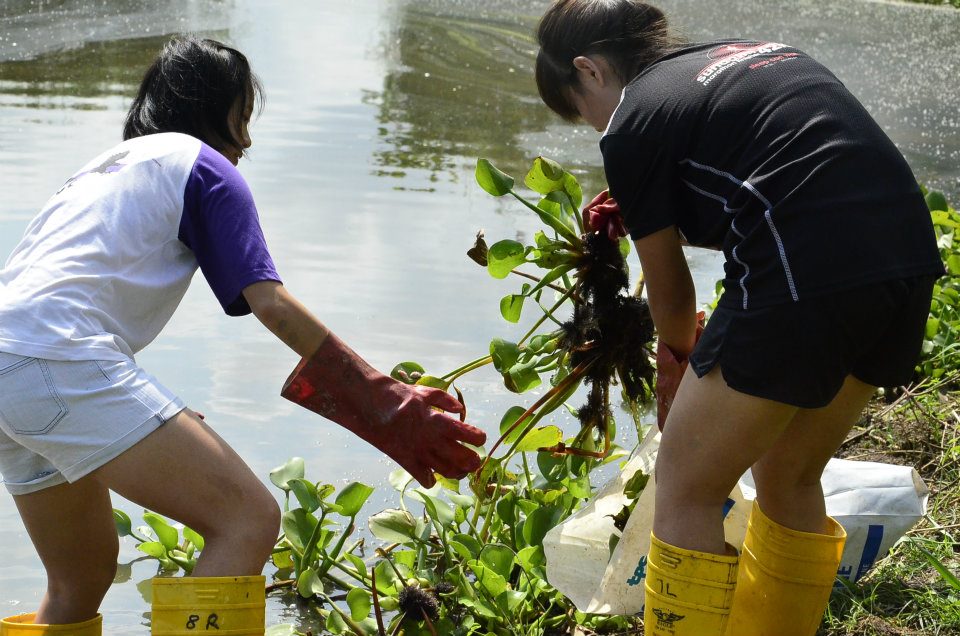 |
| Volunteers removing water hyacinth from the Kranji Bund Marshes. Photo by Xue Wei Jian. |
At the same time, pig farming was banned in water catchment areas and relocated to an intensive pig farming estate in Punggol. 19, 22 By 1977, relocation of pig farms located within the catchment of the Kranji Reservoir was completed. 19 This helped to relieve the situation by reducing nutrient input into the reservoir. 19
Even now, water hyacinth still poses a problem in the Kranji Bund Marshes along the western shore of the Kranji Reservoir. 23 The Nature Society of Singapore (NSS) adopted the Kranji Bund Marshes under the Active, Beautiful and Clean Waters Program adoption scheme in 2008. 24 Part of their pond maintenance program is to clear aquatic weeds that clog the marshes, such as water hyacinth, in order to restore the open water habitat for water birds. 24, 25 Water hyacinth is also known to speed up the rate of evapotranspiration, which could be contributing to the drying up of the Kranji Bund Marshes. 4, 10
Control Methods
There are a variety of methods employed to manage water hyacinth invasions. Usually, a number of the following methods are used in conjunction with each other. For maximum effectiveness, management programs should also involve the local community and other stakeholders to target root causes (eg high nutrient loads due to pollution). 4 There have been no instances of successful eradication of water hyacinth from an area once it is established. 26 The control methods described below only cover methods to manage an already existing water hyacinth infestation. Prevention measures such as quarantine are not described.
Physical Control
Physical control methods usually involve dredging or cutting up the weeds. 27 This can be done manually, or with machines such as aquatic weed harvesters, tugboats or vegetative cutters. Manual physical control is slow and laborious, and therefore expensive, especially in countries with high labour costs. 27 To maximize effectiveness, the plants have to be removed from the water and disposed of elsewhere to prevent the recycling of nutrients back into the water, as was the case in Kranji Reservoir in Singapore. 19 Also, the cut up plant parts may still produce clones. Rotting masses of water hyacinth could also pose a problem for water quality. 28 Moreover, the rate of physical removal needs to be able to keep up with the rate of regeneration. 29 Physical removal is the main management method employed in China, but it has been rather ineffective as the weeds were regenerating faster than they were being removed. 29There are other types of physical control which involve manipulation of the environment to prevent growth of aquatic weeds. 27, 28 For example, the drawdown method involves removing water from water bodies until a desired depth that will inhibit growth of water hyacinth. 28 This method has been found to be effective on water hyacinth infestations, but destroys the ecosystem and interferes with use of water bodies. 28
Chemical Control
Herbicides can also be used to control water hyacinth populations. Due to fears of pollution of water bodies, chemicals that can be sprayed are regulated stringently in most places. In the US, there are only 6 herbicides that are registered with and approved by the Environment Protection Agency for use in water. 28 The registration process of aquatic herbicides is costly and lengthy, taking up to U$20–40 million and 8–12 years due to extensive testing to ensure safety and determine guidelines for safe usage. 28 Herbicides do not act on the plants immediately. This means that effective chemical management of water hyacinth will need to consider not only the rate at which the herbicide acts on the plant, but also other environmental factors that determine the duration the herbicide stays in the water. 28Biological Control
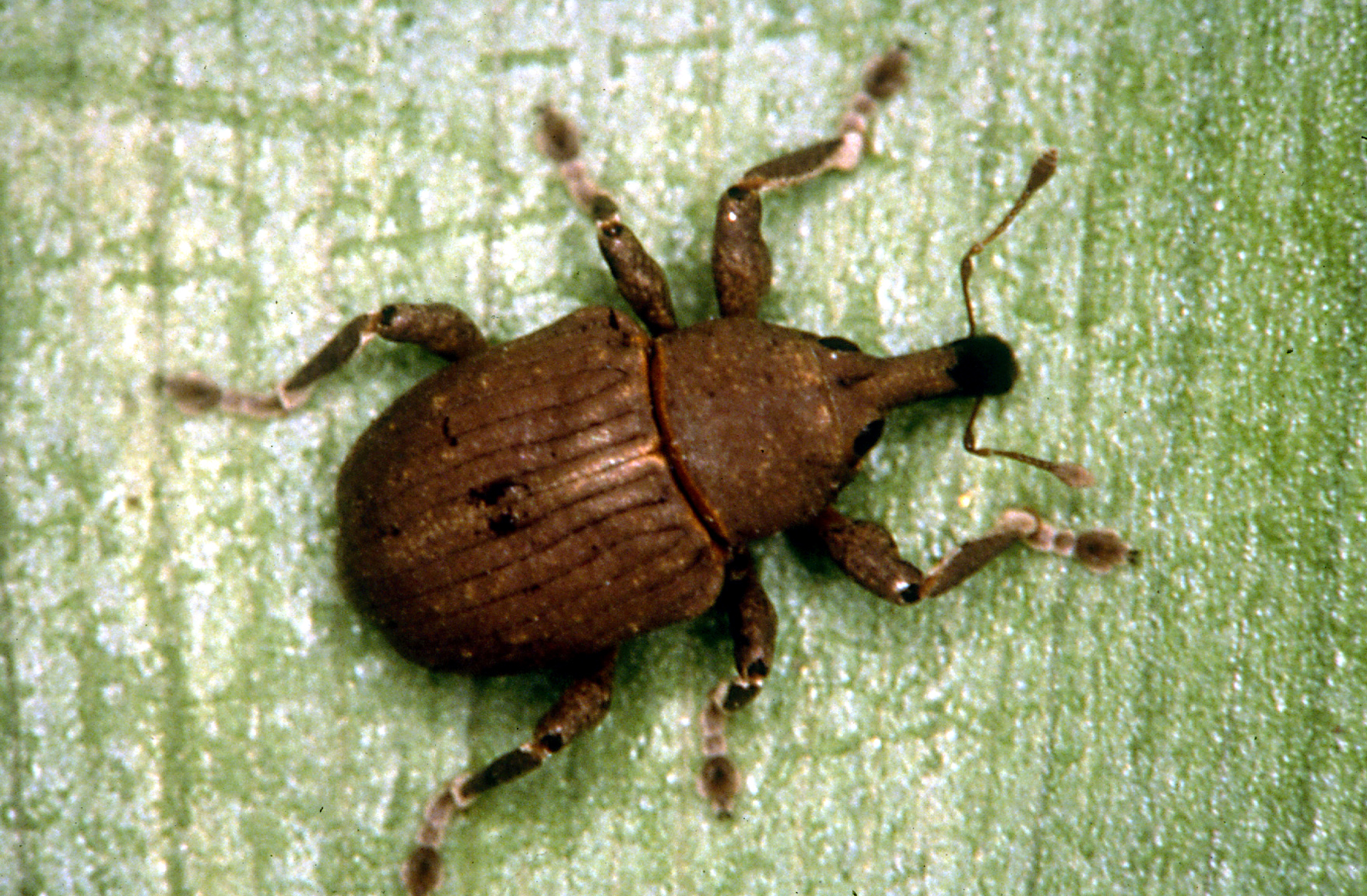 |
| Water hyacinth weevil Neochetina bruchi. Photo by CSIRO. Image from Wikimedia Commons. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. |
Two water hyacinth weevils (Neochetina eichhorniae and Neochetina bruchi) and two water hyacinth moths (Niphograpta albiguttalis and Xubida infusella) have been introduced as biological control agents in a number of countries. 4, 28 These insects were found to be host specific to water hyacinth, and can decrease plant mass and slow proliferation to some degree. 30 After the initial costs of breeding and introduction, once a certain threshold has been reached, this control method is self-sustaining. 30
Utilisation Control
Control by using the water hyacinth is not a specific control method, but an additional benefit from controlling water hyacinth invasions. 4, 26 See uses.Uses
Bioenergy Production
Water hyacinth is almost ideal for bioenergy production – it is an abundantly available perennial non-crop plant with high cellulose content and grows rapidly. 4 However, its high water content of over 90% is a disadvantage because it complicates harvesting and processing. 4 In order for water hyacinth to become commercially viable for bioenergy production, the technical difficulties and low yield caused by high water content need to be overcome first. 4, 31 Due to the expertise and specialized machinery required, it is not a practical source of alternative fuel for local communities. 31Phytoremediation
Water hyacinth has attracted considerable attention because of its ability to grow in heavily polluted water and absorb contaminants, heavy metals and excessive nutrients from the water column. 10, 31 For example, it is known to accumulate toxic metals such as lead, copper, zinc and aluminium, and organic pollutants such as phenolic compounds. 31 Moreover, water hyacinth has a high affinity for certain pollutants, and is able to accumulate them in its tissues even if they are present in trace concentrations in the water. 31 As such, water hyacinth has potential for phytoremediation in polluted and eutrophic waters, which could be cheaper than modern wastewater treatment techniques. 10 Studies have found that it is effective in treating domestic wastewater, agricultural runoff, livestock wastes and industrial effluent. 31 It has been used for removing inorganic nutrients, toxic metals and even persistent organic pollutants. 31 However, the benefits of phytoremediation have to be weighed against the possible problems that introduction of water hyacinth may bring about. 10Others
Fibers from water hyacinth stems can be used to make rope, baskets, fashion acessories and paper. 31 Several small-scale cottage industry papermaking projects have been successful in Philippines, Indonesia, and India. 31 |
| Water hyacinth bags. Image from Natural Mystique. Permission pending. |
There is even a social enterprise dedicated to making sanitary pads from water hyacinth fibers. The project aims to improve feminine sanitation for women in Africa who are unable to afford sanitary pads, while dealing with the water hyacinth problem at the same time. 32 See JaniPad for more information.
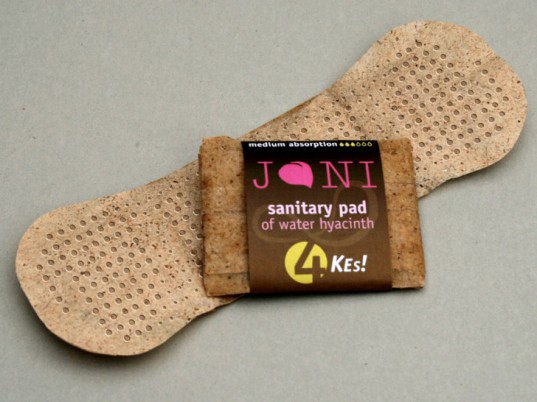 |
| Biodegradable pads made from water hyacinth. Image from JaniPad. Permission pending. |
Taxonomy
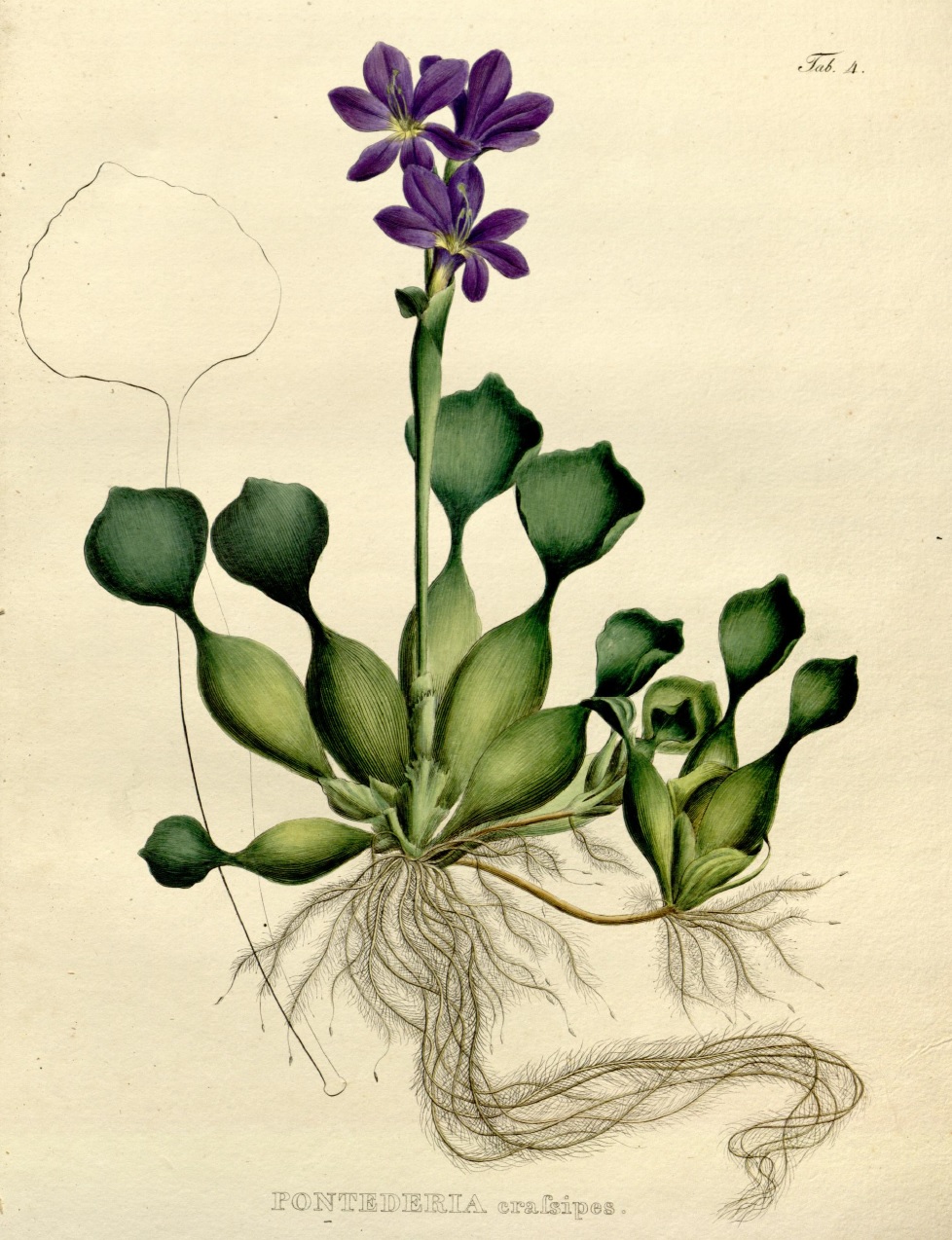 |
| Original illustration of water hyacinth. Image from Martius, 1823. Nova Genera et Species Plantarum Brasiliensium, 1: 9, plate 4. |
Vernacular name: (Common) water hyacinth
Scientific name: Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms, 1883
Synonyms: Pontederia crassipes Mart., Pontederia elongata Balf., Pontederia crassicaulis Schltdl., Eichhornia cordifolia Gand., Eichhornia crassicaulis Schltdl., Eichhornia speciosa Kunth [illegitimate], Heteranthera formosa Miq., Piaropus mesomelas Raf., Piaropus crassipes (Mart.) Raf., Pontederia crassipes Roem. & Schult. 33
History: Water hyacinth was first described by Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius (1794 – 1868), a German botanist and explorer, in 1823 under the name Pontederia crassipes. It was subsequently moved to the genus Eichhornia by Hermann Maximilian Carl Ludwig Friedrich zu Solms-Laubach (1842 - 1915), a German botanist, in 1883.
Type: Lectotypified by C. N. Horn, 1994. Pontederiaceae in Görts-van Rijn (Ed.), Flora of the Guianas, Series A: Phanerogams. Fascicle 15: 94. 1994. Supposedly located in Bahia, Brazil, Rio San Francisco near Malhada. More specific information unavailable.
Phylogeny
The following tree presents phylogenetic relationships between monocotyledons. The family Pontederiaceae, which water hyacinth is a part of, is highlighted by the red box in the diagram. The tree was constructed using matK (maturase K gene) and rbcL sequences from 113 genera of 45 families. 34 The chloroplast gene matK and protein encoding gene rbcL are two of the genes that have been proposed to be used in DNA barcoding for plants. 34, 35
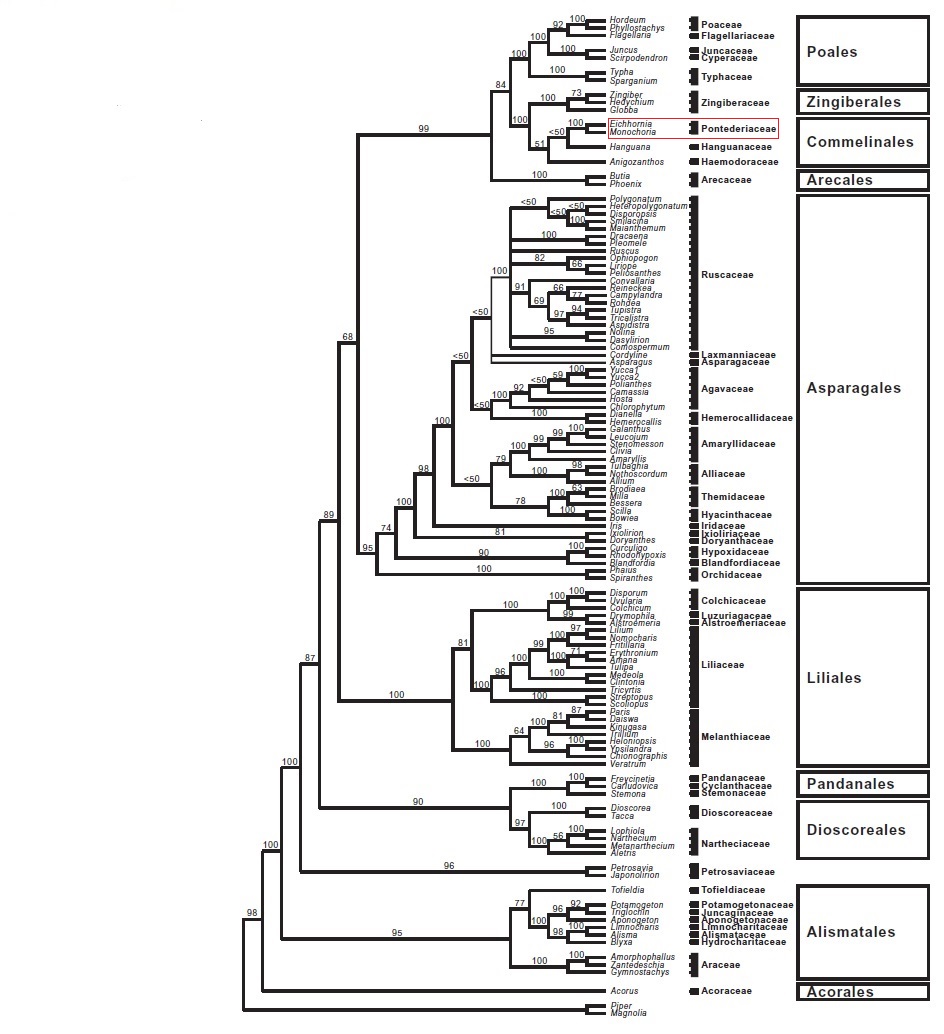 |
| Phylogenetic tree showing evolutionary relationships of monocotyledons. Adapted from Tamura, M. N, Yamashita, J., Fuse, S. & Haraguchi, M., 2004. Molecular phylogeny of monocotyledons inferred from combined analysis of plastid matK and rbcL gene sequences. Journal of Plant Research, 117:109–120. |
The multiple studies have been done on the phylogeny of the family Pontederiaceae using different genes. There does not appear to be much consensus in the results of the different studies. The following trees show tree shows water hyacinth's position in the family Pontederiaceae. For more information on the trees, see original article for the tree on the left, and see original article for the tree on the right. 36, 37 Please note that the trees do not include all species in the family Pontederiaceae.
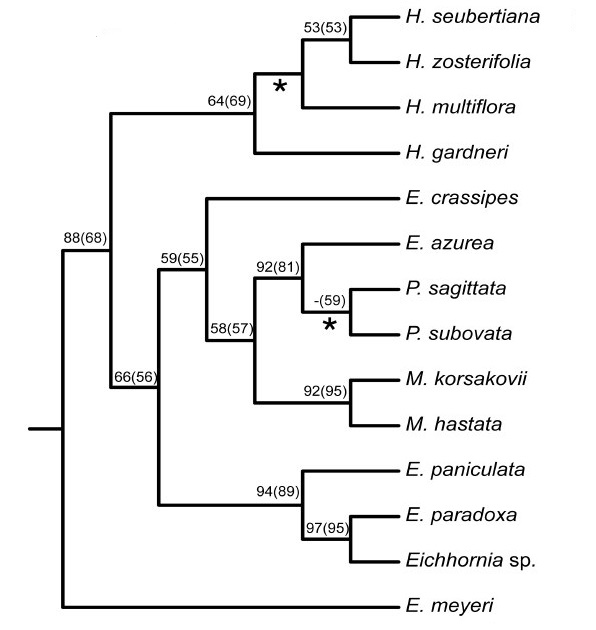 |
| Phylogenetic tree of Pontederiaceae. Adapted from Ness R. W., Graham, S. W. & Barrett, S. C. H., 2011. Reconciling gene and genome duplication events: Using multiple nuclear gene families to infer the phylogeny of the aquatic plant family Pontederiaceae. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(11): 3009–3018. |
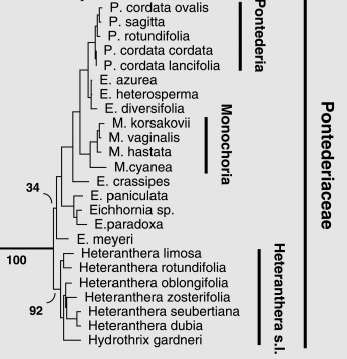 |
| Phylogenetic tree of Pontederiaceae. Graham, S. W., Olmstead, R. G. & Barrett, S. C. H., 2002. Rooting phylogenetic trees with distant outgroups: A case study from the Commelinoid Monocots. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 19(10): 1769–1781. |
References
[1] “Species information: Eichhornia crassipes” by Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. Flora of Zimbabwe, 2014. URL: http://www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/species.php?species_id=112960 (accessed 21 November 2014).
[2] Gopal B. 1987. Water hyacinth. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
[3] “Eichhornia crassipes (aquatic plant)”, by Invasive Species Specialist Group [ISSG]. Global Invasive Species Database, 04 Aug 2006. URL: http://www.issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=70&fr=1&sts=&lang=EN (accessed 10 Oct 2014).
[4] United National Environment Programme (UNEP), 2013. Water hyacinth: Can its aggressive invasion be controlled? URL: http://na.unep.net/geas/getUNEPPageWithArticleIDScript.php?article_id=98 (accessed 5 Nov 2014).
[5] Téllez, T., López, E., Granado, G., Pérez, E., López, R. & Guzmán, J., 2008. The water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes: an invasive plant in the Guadiana River Basin (Spain). Aquatic Invasions 3(1): 42-53.
[6] Ministry for Primary Industries, 2013. Water hyacinth. URL: http://www.biosecurity.govt.nz/files/pests/water-hyacinth/water-hyacinth-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed 11 Nov 2014).
[7] Australian Weeds Committee, 2012. Water hyacinth: National strategy 2012 to 2017. URL:
http://www.weeds.org.au/WoNS/waterhyacinth/docs/National_Water_Hyacinth_Strategic_Plan_%28final-June_2013%29.pdf (accessed 11 Nov 2014).
[8] “Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)”, by NSW Department of Primary Industries, Mar 2010. Department of Primary Industries. URL: http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/agriculture/pests-weeds/weeds/profiles/water-hyacinth (accessed 5 Nov 2014).
[9] “Eichhornia crassipes”, by Missouri Botanical Garden, n.d. Missouri Botanical Garden. URL: http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=285493&isprofile=0&letter=E (accessed 5 Nov 2014)
[10] Villamagna, A. M. & Murphy, B. R., 2010. Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A review. Freshwater Biology, 55(2): 282–298.
[11] Barrett S.C.H. 1980. Sexual reproduction in Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth). 1. Fertility of clones from diverse regions. Journal of Applied Ecology 17(1):101-112.
[12] Barrett S.C.H. 1980. Sexual reproduction in Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth). II. Seed production in natural populations. Journal of Applied Ecology 17(1):113-124.
[13] Batanouny, K. H. & El-Fiky, A. M., 1975. The water hyacinth (Eichhyornia crassipes solms) in the Nile system, Egypt. Aquatic Botany, 1: 243–252
[14] United Nations Environmental Program [UNEP], 2006. Africa environment outlook 2: Our environment, our wealth. URL:
http://www.unep.org/DEWA/Africa/docs/en/AEO2_Our_Environ_Our_Wealth.pdf (accessed 12 Nov, 2014).
[15] Ayodo, T. & Jagero, N., 2012. The economic, educational and social responsibilities of elders development groups in Lake Victoria region. Academic Research International, 2 (3): 610-620.
[16] MWBP/RSCP, 2006. Invasive alien species in the Lower Mekong Basin: Current state of play. Mekong Wetland Biodiversity Programme and Regional Species Conservation Programme, The World Conservation Union (IUCN). URL: http://cmsdata.iucn.org/downloads/mlb_ias_current_state_of_play.pdf (accesed 12 Nov 2014).
[17] Patel, S., 2012. Threats, management and envisaged utilizations of aquatic weed Eichhornia crassipes: An overview. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 11: 249–259.
[18] Mailu, A., 2001. Preliminary assessment of the social, economic and environmental impacts of water hyacinth in the Lake Victoria basin and the status of control. In: Biological and integrated control of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes. ACIAR Proceedings No. 102.
[19] Wee, Y. C. & Corlett, R., 1986. The city and the forest: Plant life in urban Singapore. Singapore: Singapore University Press.
[20] "The 'aliens' in Singapore”, by Lim, K. S. Nature Watch, Sep 1998. URL: http://habitatnews.nus.edu.sg/pub/naturewatch/text/a063b.htm (accessed on 29 Oct 2014).
[21] Public Utilities Board [PUB], 2013. PUB annual report 2012/ 2013: Commemorating 50 years of water from the first drop. URL:
http://www.pub.gov.sg/annualreport2013/PUB_AR13_web.pdf (accessed on 29 Oct 2014).
[22] "History: Our past - The Primary Production Department”, by Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority (AVA). Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority of Singapore, 17 Jan 2014. URL: http://www.ava.gov.sg/AboutAVA/History/ (accessed 1 Nov 2014).
[23] "Kranji bund marshes”, by Ho, H. C. Nature Watch, Apr 2002. URL: http://habitatnews.nus.edu.sg/pub/naturewatch/text/a102a.htm (accessed 1 Nov 2014).
[24] "NSS Kranji Reservoir Adoption Program and Ceremony”, by Jain, A. Nature Society of Singapore, 29 Nov 2008. URL: http://www.nss.org.sg/news.aspx?id=5vEi7KzOmTk4yPUM=&group_id=ohgTSSH5Yo0 (accessed 1 Nov 2014).
[25] “Pond restoration - The heroes at work”, by Jain, A. Nature Society of Singapore, 27 Sep 2009. URL: http://www.nss.org.sg/news.aspx?id=EkbZMDlgPII=&group_id=ohgTSSH5Yo0 (accessed 1 Nov 2014).
[26] European Environment Agency, 2012. The impacts of invasive alien species in Europe. URL: http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/impacts-of-invasive-alien-species (accessed 16 Nov 2014).
[27] Murphy, K. J., 1988. Aquatic weed problems and their management: A review. II. Physical control measures. Crop Protection, 7: 283-302.
[28] Madsen, J. D., 1997. Methods for management of nonindigenous aquatic plants. In Luken, J. O. & Thieret, W. T. (Eds.), Assessment and management of plant invasions (pp. 145-170). New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
[29] Lu, J., Wu, J. & Zhu, L. 2007. Water hyacinth in China: A sustainability science-based management framework. Environmental Management, 40:823–830.
[30] Ochiel, G. R. S. & Stephen W Njoka, S. W., 2012. Biological control and monitoring of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes, Marts. Solms-Laubach (Liliales: Ponteridiaceae) during the post-resurgence period in Lake Victoria basin, Kenya. URL: http://195.202.82.11:8080/jspui/handle/123456789/31 (accessed 16 Nov 2014).
[31] Malik, A., 2007. Environmental challenge vis a vis opportunity: The case of water hyacinth. Environment International 33(1):122–138.
[32] Lidman, K., Thornander, S., Hoogendijk, M., Vedeler, L. M. & Tobiassen K. 2009. New sense in nuisance. URL http://www.janipad.com/Jani_report.pdf (accessed 12 Nov 2014).
[33] “Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms”, by The Plant List. The Plant List, 2010. URL: http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-242133 (accessed 5 Nov 2014).
[34] Tamura, M. N, Yamashita, J., Fuse, S. & Haraguchi, M., 2004. Molecular phylogeny of monocotyledons inferred from combined analysis of plastid matK and rbcL gene sequences. Journal of Plant Research, 117:109–120.
[35] Yu, J., Xue, J. H., & Zhou, S. L. 2011. New universal matK primers for DNA barcoding angiosperms. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49(3): 176–181.
[36] Ness R. W., Graham, S. W. & Barrett, S. C. H., 2011. Reconciling gene and genome duplication events: Using multiple nuclear gene families to infer the phylogeny of the aquatic plant family Pontederiaceae. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(11): 3009–3018.
[37] Graham, S. W., Olmstead, R. G. & Barrett, S. C. H., 2002. Rooting phylogenetic trees with distant outgroups: A case study from the Commelinoid Monocots. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 19(10): 1769–1781.